Your brain’s natural tendency to find patterns and interpret ambiguous stimuli, like pareidolia, leads you to see faces or shapes where none exist. Memories can be distorted by trauma or cultural stories, fueling ghost stories you believe over time. Cognitive biases, like confirmation bias, reinforce these beliefs. Evolutionary survival instincts make you alert to unknown dangers, while media and storytelling further embed these myths. Understanding these processes helps explain why ghost myths persist—more insights await if you keep exploring.
Key Takeaways
- Human pattern recognition and pareidolia cause misinterpretations of ambiguous stimuli as ghosts or spirits.
- Cultural narratives, media portrayals, and folklore reinforce beliefs, making ghost myths more persistent over generations.
- Cognitive biases like confirmation bias and illusory correlations sustain and strengthen supernatural beliefs despite skepticism.
- Evolutionary fear responses and innate sensitivity to uncertainty promote vigilance and interpret ambiguous cues as supernatural threats.
- Memory distortions and emotional trauma influence the recollection and storytelling of ghost experiences, maintaining their cultural significance.
The Brain’s Pattern Recognition and Pareidolia
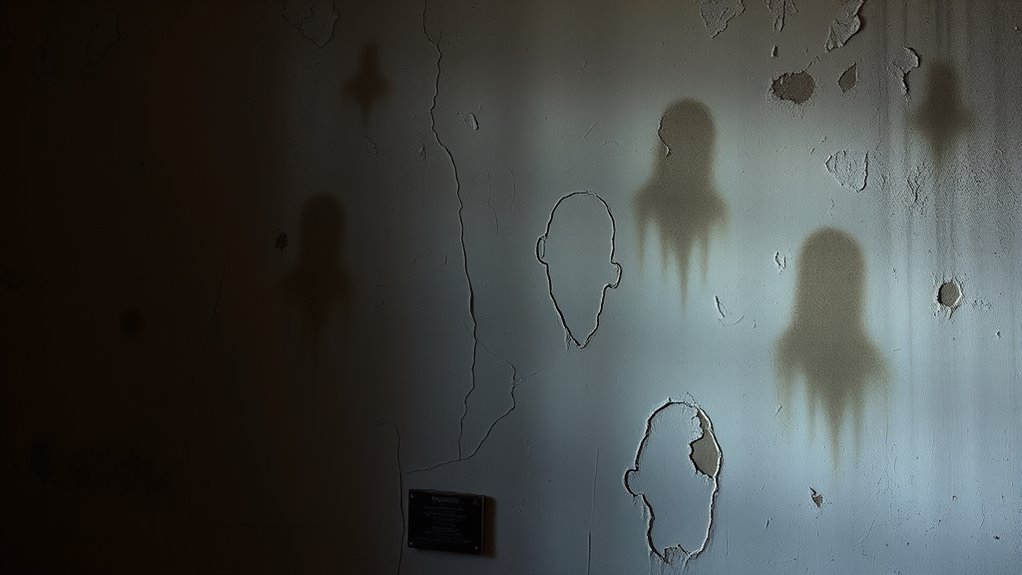
Because our brains are wired to seek out familiar patterns, they often interpret ambiguous stimuli as meaningful shapes or images. This tendency, known as pareidolia, means you might see faces in clouds, shadows in the dark, or random objects that resemble something familiar. Your brain constantly searches for patterns to make sense of the world, even when there’s no real meaning behind what you see. This automatic process helps you recognize important cues quickly, but it can also lead to false perceptions. When faced with unclear or confusing visuals, your mind fills in gaps based on past experiences and expectations. That’s why you might perceive a vague shape as a ghostly figure, reinforcing supernatural beliefs without any real evidence. Additionally, understanding auditory illusions can shed light on how our perception can be easily deceived across different senses.
Memory, Trauma, and the Creation of Ghost Stories

Your memories aren’t always accurate and can be influenced by trauma, which shapes how you interpret events. When you experience distress or loss, your mind may create ghost stories as a way to process those feelings. Understanding this connection helps explain why trauma often leads to vivid, lasting hauntings in stories and beliefs. Modern AI security solutions also use advanced pattern analysis to distinguish genuine threats from false alarms, reflecting how trauma can distort perception.
Memory Distortion and Ghosts
Memory distortion plays a crucial role in how ghost stories develop, especially when trauma influences perception. When you recall a haunting event, your mind may fill in gaps or alter details, making the experience seem more vivid or frightening than it was. Emotional intensity can distort your memory, causing you to remember shadows or noises as supernatural phenomena. Over time, these altered memories become ingrained, fueling belief in ghostly encounters. This process isn’t intentional; it’s a natural consequence of how memory works. Your brain prioritizes emotionally charged details, often at the expense of accuracy. Additionally, segment audience for targeted campaigns based on behavior and preferences can reinforce these memories by repeatedly exposing individuals to similar stories. As a result, stories evolve, blending fact and fiction, and contributing to the persistent myth of ghosts in cultural narratives.
Trauma’s Role in Hauntings
Trauma can profoundly shape the way haunted experiences are remembered and interpreted. When you experience intense fear or grief, your brain may encode these moments more vividly, making them seem more real over time. Traumatic events often lead to heightened suggestibility, where your mind fills in gaps or interprets ambiguous stimuli as paranormal. This means that if you’ve suffered loss or violence, you’re more likely to perceive unexplained noises or apparitions as ghosts. The emotional weight of trauma can also distort memories, causing you to remember certain details more dramatically. These factors contribute to how haunted stories develop, blurring the line between genuine supernatural encounters and psychological responses rooted in trauma. Additionally, the brain’s memory encoding processes can become biased by emotional states, further reinforcing belief in paranormal phenomena. Ultimately, trauma influences not just what you remember but how you interpret those memories as ghostly phenomena.
The Role of Cultural Narratives and Social Learning

Cultural narratives shape how societies interpret and perpetuate ghost myths, often through stories, rituals, and media that reinforce certain beliefs. You encounter these stories from childhood, hearing tales of spirits and hauntings that become part of your cultural fabric. Media like movies, books, and folklore continually reinforce the idea that ghosts are real and tied to unresolved issues or past traumas. Rituals and traditions provide communal reinforcement, making belief in ghosts feel like a shared truth. Through social learning, you absorb these narratives, which influence your perceptions and expectations about unexplained phenomena. Cultural frameworks create a context where ghost myths persist, even in the face of scientific explanations. Your environment and social interactions play a crucial role in shaping and maintaining these long-standing beliefs.
Cognitive Biases That Reinforce Belief in the Supernatural

Beliefs in ghosts and other supernatural phenomena are often reinforced by the way our minds naturally process information. Cognitive biases, like pattern recognition, lead you to see connections where none exist, making ambiguous events seem meaningful or supernatural. Confirmation bias causes you to focus on experiences that support your beliefs while dismissing evidence against them. The bias of outgroup homogeneity makes you perceive outsiders or skeptics as uniformly dismissive, strengthening your conviction. Additionally, the tendency of illusory correlations links unrelated events—like a creaky house and a ghost sighting—creating a false sense of causality. These biases shape your perceptions, making supernatural explanations feel more plausible and persistent, even in the face of scientific skepticism. Moreover, understanding visual processing can reveal how our perception of images and scenes might be manipulated or misinterpreted, reinforcing supernatural beliefs.
Perception, Sensory Processing, and Hallucinations
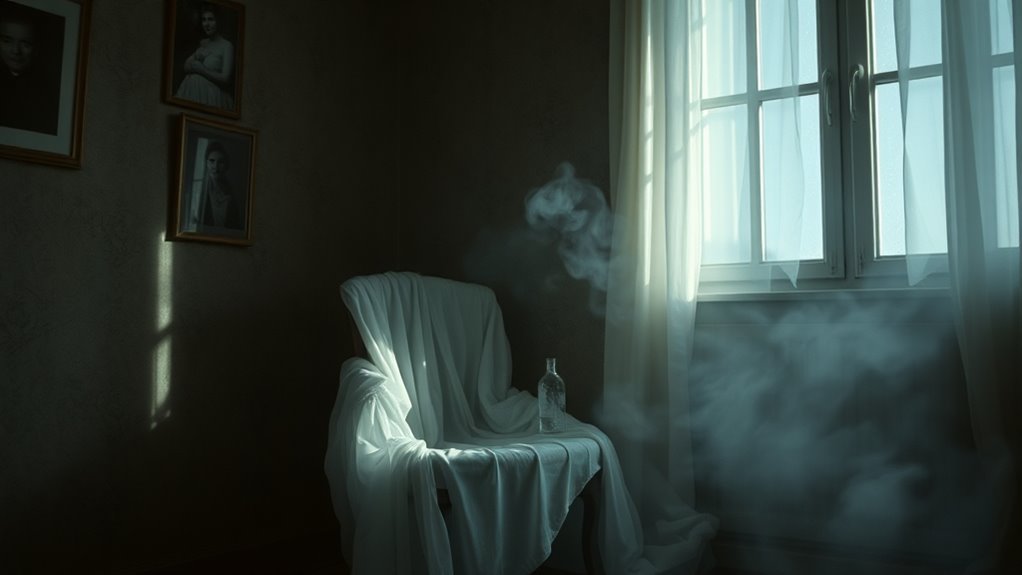

Your perception of the world around you is shaped by complex sensory processing that can sometimes lead to false impressions. Your senses gather information from light, sound, touch, and other stimuli, which your brain then interprets. Sometimes, this interpretation goes awry, causing hallucinations—perceptions without external stimuli. These can be vivid and convincing, especially in low-light environments or during moments of stress or fatigue. Your brain fills in gaps or misreads signals, creating experiences like seeing shadows or hearing whispers that aren’t real. Hallucinations aren’t limited to mental health issues; they can also result from sensory deprivation, medication, or extreme emotional states. Moreover, certain sensory processing conditions can heighten the likelihood of experiencing hallucinations. Understanding how your senses work helps explain why your mind might sometimes perceive ghosts or supernatural entities that aren’t actually present.
Evolutionary Perspectives on Fear and the Unknown

Your fear of the unknown likely evolved as a survival trait, helping early humans avoid danger and stay alive. This innate sensitivity to uncertainty keeps you alert to potential threats even today. Recognizing this bias can help you understand why supernatural fears, like ghosts, continue to persist.
Fear as Survival Trait
Fear functions as a crucial survival trait because it triggers immediate responses that help us avoid danger. When you sense a threat, fear activates your fight-or-flight response, preparing you to confront or escape. This instinct increases your chances of survival by sharpening your awareness and reactions. Additionally, understanding emotional responses can help us better manage fear and its effects on behavior. Here are four ways fear benefits you:
- Detects threats early, so you can respond swiftly.
- Increases alertness, sharpening your senses.
- Prepares your body with adrenaline, boosting strength and speed.
- Encourages caution, helping you avoid risky situations.
This instinctive response has been essential throughout evolution, shaping how humans react to potential dangers. It’s why fear remains deeply ingrained, guiding behaviors that enhance survival odds in uncertain environments.
Innate Sensitivity to Uncertainty
Humans are inherently sensitive to uncertainty because our evolutionary history has favored responses that prioritize caution in unfamiliar situations. When faced with the unknown, your brain instinctively searches for patterns or explanations, even if none exist. This sensitivity helps you avoid potential threats, as unfamiliar environments could hide dangers. Over time, this trait became ingrained, making you more prone to perceive ambiguous stimuli as threatening or supernatural. Your mind seeks certainty, often filling gaps with guesses rooted in fear or superstition. This innate alertness to uncertainty explains why ghost myths persist across cultures—your brain’s natural tendency to interpret the unexplained as something supernatural. In essence, your evolutionary wiring pushes you toward vigilance, especially in situations where certainty is lacking. Additionally, this heightened sensitivity can influence how you interpret ambiguous stimuli, leading to the perception of supernatural entities or phenomena.
The Impact of Media and Storytelling on Ghost Myth Persistence
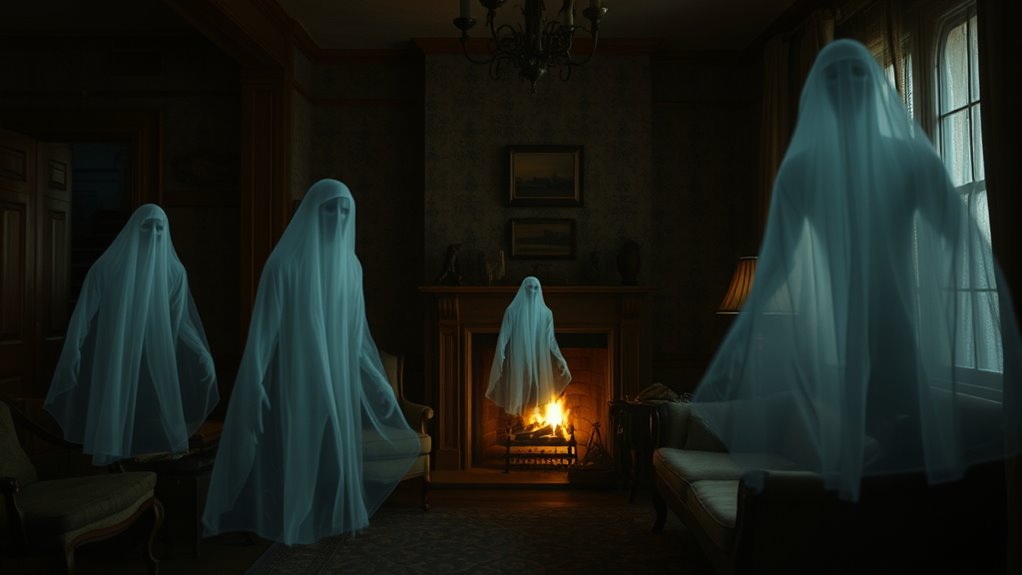

Media and storytelling play a pivotal role in shaping and maintaining ghost myths, often reinforcing their presence in cultural consciousness. Through movies, books, and TV shows, you encounter vivid stories that embed ghostly ideas into your mind. These narratives often emphasize eerie atmospheres and unexplained phenomena, making ghosts seem more real. Consider these impacts:
- They create memorable imagery that sticks in your memory.
- They associate ghost sightings with specific locations or events.
- They reinforce cultural stereotypes about spirits and hauntings.
- They blur the line between fiction and reality, encouraging belief.
- They can influence perceptions through antioxidants and other health-related concepts that subtly shape how stories are perceived and remembered.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Individual Differences Influence Belief in Ghost Phenomena?
Your individual differences, like personality traits, prior beliefs, and cognitive biases, strongly influence your belief in ghost phenomena. If you’re naturally more imaginative or prone to suggestibility, you’re more likely to accept ghost stories. Your cultural background and personal experiences also shape your perceptions, making you more receptive or skeptical. These differences mean that some people are more inclined to believe in ghosts, while others remain unconvinced.
Can Cognitive Science Explain Why Some People Are More Prone to Ghost Sightings?
You can’t ignore that cognitive science explains why some people are more prone to ghost sightings. Your brain’s tendency for pareidolia, the tendency to see patterns or faces in randomness, makes you more likely to interpret ambiguous stimuli as supernatural. Additionally, your expectations, cultural background, and suggestibility influence your perception, leading you to see ghosts even when no one else does. These mental processes shape your experiences and beliefs profoundly.
What Neurological Conditions Might Mimic Experiences Attributed to Ghosts?
You might experience sensations attributed to ghosts if you have neurological conditions like temporal lobe epilepsy, which can cause hallucinations or unusual perceptions. Migraine auras can also produce visual or sensory disturbances that feel like ghostly encounters. Sleep paralysis, often linked to narcolepsy or disrupted sleep, can lead you to see or feel a presence, making you believe in supernatural entities. These conditions alter brain activity, mimicking ghostly experiences.
How Does Language Shape Our Understanding and Storytelling of Ghost Myths?
Language shapes your understanding of ghost myths by framing how you interpret mysterious events. The words you use influence your perception, making stories more vivid and believable. When you tell or hear tales with specific language, it reinforces cultural beliefs and emotional responses. Your storytelling reflects shared ideas, and nuanced language can evoke fear or wonder, guiding how you interpret unexplained phenomena and perpetuate ghost myths across generations.
Are There Evolutionary Advantages to Believing in Supernatural Entities?
Believing in supernatural entities can give you an evolutionary edge by helping you stay alert to potential dangers and fostering social cohesion. When you imagine spirits or ghosts, you’re more likely to heed warnings and stick with your group, which boosts survival chances. It’s a case of killing two birds with one stone—enhancing safety and strengthening bonds—making these beliefs an advantageous part of human evolution.
Conclusion
Just like a fire that keeps burning long after the sparks fade, ghost myths persist because your brain is wired to find patterns and meaning in the unknown. Your memories, cultural stories, and biases all feed into this ongoing illusion, making the supernatural feel real. By understanding these cognitive quirks, you can see how these stories stay alive—like echoes bouncing in a canyon—long after the initial experience is gone.









