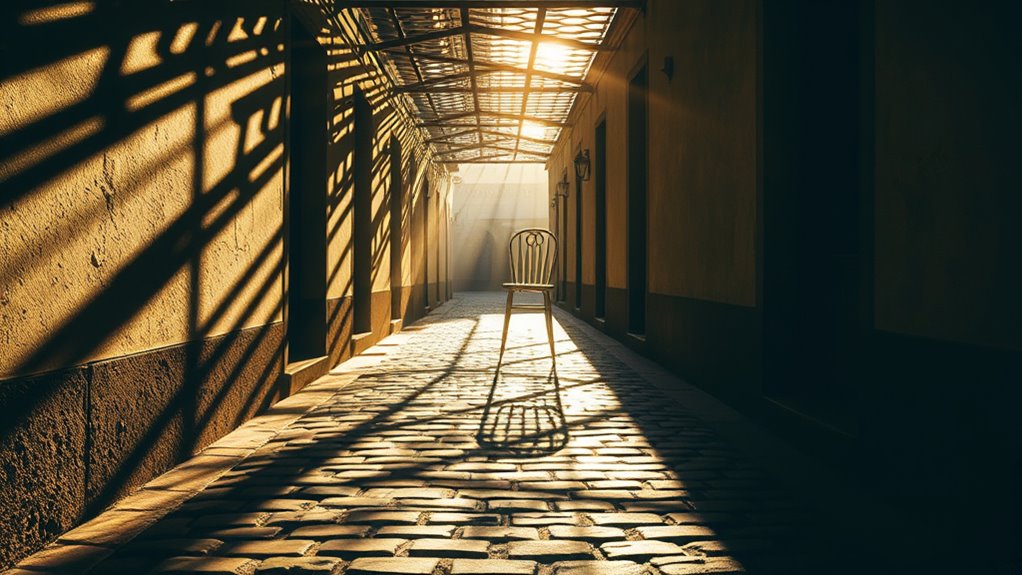
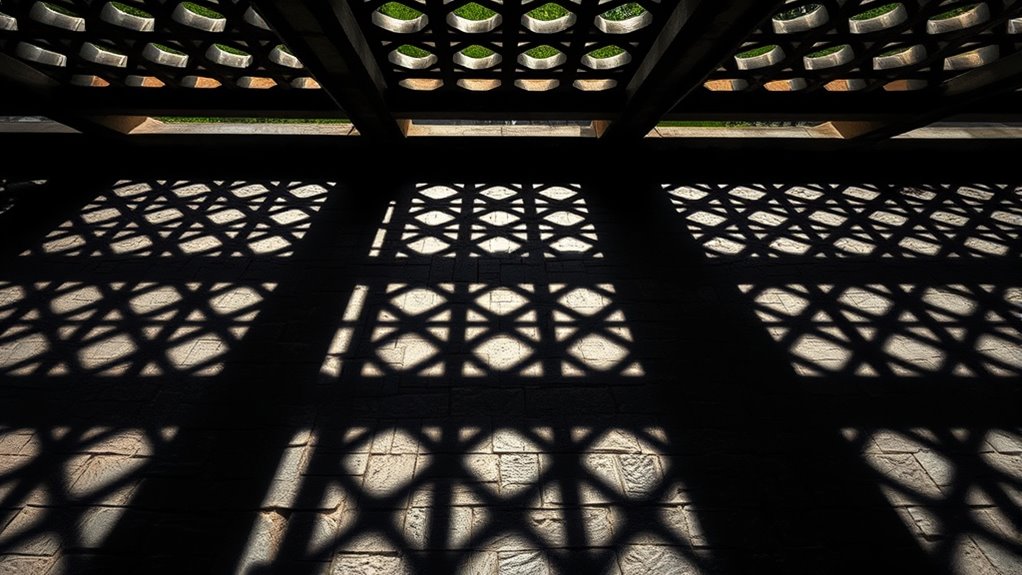
Light, shadows, and your expectations work together to shape what you see, often creating illusions. Light guides your eyes and highlights details, while shadows suggest depth, shape, or hidden objects. Your brain interprets these cues based on past experiences and surroundings, sometimes filling in gaps or misjudging distances. By understanding how these elements influence perception, you’ll discover how illusions trick your mind and distort reality—continue onward to uncover how this fascinating process unfolds.
Key Takeaways
- Light guides perception by highlighting details, creating shadows, and influencing depth, which can deceive the brain into seeing three-dimensional forms.
- Shadows reveal hidden object features, sizes, and positions, altering perception based on their shape, size, and angle.
- Expectations and past experiences fill in gaps, causing the brain to interpret ambiguous visual cues as specific shapes or patterns.
- Lighting angles, contrast, and environment cues work together to produce illusions of size, distance, and motion.
- Perception is a mental construction shaped by light, shadows, and expectations, often leading to visual illusions and misinterpretations.

Lampat Dimmable LED Desk Lamp, 4 Lighting Modes (Reading/Studying/Relaxation/Bedtime), 5-Level Dimmer, Touch-Sensitive Control Panel, 1-Hour Auto Timer, 5V/1A USB Charging Port, Piano Black
Four Lighting Modes: Choose from Reading, Studying, Relaxation, and Bedtime modes to suit different activities and moods.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
The Role of Light in Perceptual Tricks

Light is the fundamental element that shapes how we perceive the world around us. It guides our eyes, highlights details, and influences our perception of depth and shape. When light hits an object, your brain interprets its brightness, shadows, and reflections to understand what you’re seeing. Subtle changes in lighting can make flat surfaces appear three-dimensional or obscure details entirely. For example, bright light can wash out features, while shadows can create illusions of depth or form. You rely on consistent lighting cues to recognize familiar objects, but when light behaves unexpectedly, your perception can deceive you. Additionally, the way light interacts with home furnishings can significantly alter how a space feels and appears, influencing visual perception and mood. Virtually, light acts as a silent artist, sculpting your visual reality and setting the stage for illusions to emerge.

RALENO Softbox Photography Lighting Kit, 16'' x 16'' Softbox Lighting for TikTok with LED Bulb (50W | 5500K | 97 CRI | TLCI≥97), Continuous Light for Video Recording & Photography Shooting
COMPACT & DELICATE SOFTBOX: Are you looking for a compact and delicate softbox kit? Then the 16×16-inch softbox…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
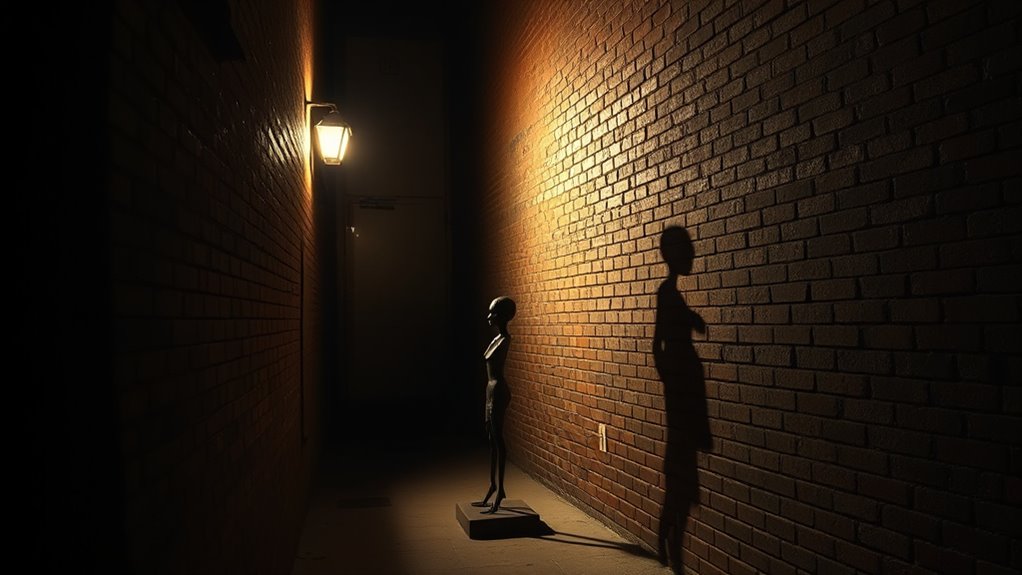
Shadows as Hidden Cues

Shadows often hide clues you might not notice at first glance, revealing details about objects and their environment. They can change in shape and size depending on the angle and light, influencing how you perceive what you’re seeing. Keep in mind that your context or surroundings can alter how shadows are interpreted, shaping your perception in surprising ways. In the realm of financial planning, understanding how inflation protection works can help you make more informed decisions about your investments and retirement strategies.
Shadows Reveal Hidden Clues
When objects cast shadows, they often reveal more than meets the eye, providing subtle clues about hidden details. Shadows can hint at the shape, texture, or movement of an object that’s not immediately visible. For example, a shadow’s length and angle can suggest an object’s size or position, while irregular edges might indicate roughness or complexity. In detective work or art, shadows serve as silent clues, guiding your instincts and observations. They can obscure or distort features, prompting you to look closer and interpret what’s concealed. By paying attention to these shadowy hints, you uncover secrets that aren’t obvious at first glance. Shadows, hence, act as hidden cues, inviting you to read between the lines and reveal what’s beneath the surface. Additionally, understanding how visual cues are interpreted can enhance your ability to read these subtle signals effectively.
Shape and Size Variations
Because shadows change in shape and size depending on the angle and distance of the object, they can reveal hidden details that might otherwise go unnoticed. When you observe shadows, you might notice how elongation or compression hints at the object’s position or orientation. A tall, narrow shadow suggests the object is low and near, while a broad, diffuse shadow indicates it’s higher or farther away. Variations in shadow size can also reveal subtle differences in the object’s dimensions, especially when lighting conditions shift. By paying close attention to these shape and size changes, you can infer information about objects even if they’re partially obscured. Shadows, hence, serve as powerful cues, allowing you to interpret spatial relationships and hidden features through their dynamic transformations. Additionally, understanding how contrast ratio affects shadow detail can help you better recognize subtle features within the shadows themselves.
Context Alters Perception
Our perception of shadows is heavily influenced by the context in which they appear, often leading us to interpret their meaning differently based on surrounding cues. When shadows fall on familiar objects or scenes, your brain uses background information to fill in gaps, making ambiguous shapes more recognizable. For example, a shadow cast in a dimly lit alley might seem threatening, but the same shadow in a well-lit park feels harmless. Your mind constantly compares shadows to nearby objects, adjusting perceptions accordingly. Lighting angles, background textures, and environmental cues all shape how you interpret shadows as either revealing hidden details or concealing information. This contextual awareness can create illusions where shadows seem to communicate more than they actually do, guiding your perception based on the scene’s overall setting. Additionally, lighting conditions play a crucial role in how shadows are perceived, further influencing the illusion of depth and mystery.

Linkax Soccer Gifts for Teens Boys Girls, Soccer Ball 3D Illusion Lamp Night Light Room Decor, 16 Colors Change 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Year Old Boy Sports Fan Birthday Easter Gifts
Perfect School Supplies Soccer Gifts Ideas: If your child likes soccer or is a sports fan, then this…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
The Power of Contrast and Brightness
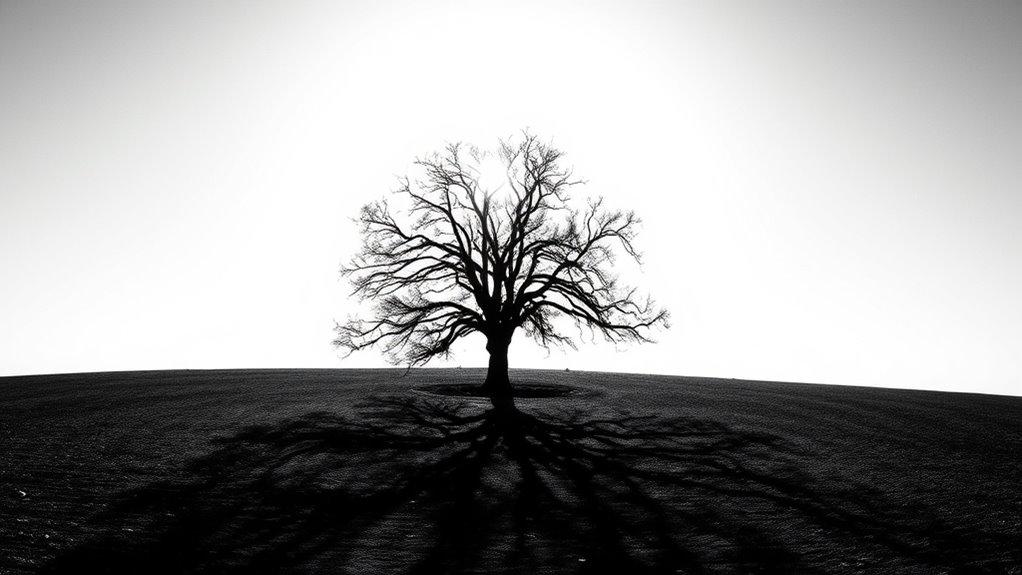

You can dramatically alter how an image is perceived by adjusting brightness and contrast. Brightness manipulation techniques make objects appear closer or farther away, while contrast enhances the visual impact of details. Understanding these effects helps you recognize how subtle changes can create powerful illusions. Additionally, dynamic communication exercises for couples can help improve understanding and connection, influencing how visual cues are interpreted in social interactions.
Brightness Manipulation Techniques
Brightness manipulation techniques hinge on the strategic use of contrast and luminance to create striking illusions. By adjusting the brightness levels in your visuals, you can make objects appear closer, larger, or more vibrant than they truly are. Increasing luminance around key areas draws attention and guides the viewer’s focus, making certain elements pop. Conversely, dimming or darkening backgrounds pushes other parts into the background, creating depth and separation. Subtle shifts in brightness can also trick your eye into perceiving movement or change where none exists. You might use gradients or gradual light progressions to enhance the illusion of three-dimensionality or to draw the eye smoothly across a scene. Mastering these techniques allows you to craft compelling illusions that manipulate perception effortlessly. Additionally, understanding the impact of highly recommended anime films can inspire creative visual storytelling and illusion techniques.
Contrast’s Visual Impact
Contrast amplifies the effects of brightness manipulation by defining the boundaries between objects and backgrounds. It sharpens distinctions, making elements stand out or blend in based on their differences. High contrast draws your eye, emphasizing key features, while low contrast creates subtle transitions that can deceive your perception. This dynamic influences how you interpret shapes, depth, and spatial relationships. By adjusting contrast levels, you can make images appear more vibrant or muted, affecting your emotional response. The following table illustrates how different contrast settings impact visual perception:
| Contrast Level | Visual Effect |
|---|---|
| Low | Soft, subdued, blending smoothly |
| Moderate | Balanced, clear but gentle outlines |
| High | Sharp, intense distinctions |
| Extreme | Stark, dramatic visual separation |
| Inverted | Reverses light and dark relationships |
Additionally, understanding visual perception can help you optimize the use of contrast in various artistic and practical applications.

Sunset LED Lamp Projector, 21 Colors Changing App & Remote Control Mood lighting, Music Sync Ambiance Lighting, Sunset Lamp for Bedroom, Living Room, Aesthetic Room Decor, Birthday Gifts for Women
【Keep the Sunset at Home】Beautiful sunsets are fleeting, and with this led lights, you don't have to travel…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
How Our Visual System Interprets Shadows
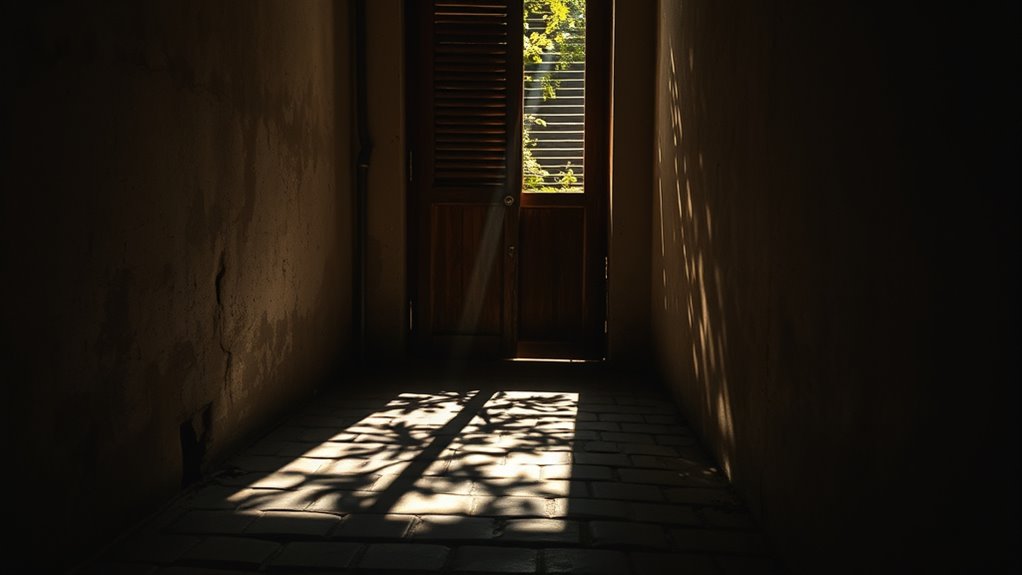

Our visual system constantly interprets shadows to understand the shapes and positions of objects in our environment. Shadows provide essential cues that help you distinguish between nearby and distant objects, identify movement, and perceive depth. When you see a shadow, your brain quickly analyzes its shape, size, and direction to infer what’s casting it. This process involves three key functions:
Shadows help us perceive shape, depth, and movement by revealing object contours and light source positions.
- Recognizing the object’s contour based on shadow edges.
- Estimating the light source’s position to interpret shadow angles.
- Inferring the object’s volume and spatial relation to other objects.
Additionally, lighting conditions influence how shadows are perceived, affecting the accuracy of depth and shape interpretation.
The Influence of Expectations on Perception

Expectations shape how you interpret visual information, often influencing what you see more than the actual stimuli do. When you expect to see a familiar object or scene, your brain fills in gaps and adjusts perceptions accordingly. This mental framework can lead you to perceive things that aren’t really there or overlook details that don’t match your expectations. For example, if you anticipate a certain pattern or shape, you’re more likely to interpret ambiguous visuals in that way. Your prior experiences, beliefs, and context all play a role in shaping these expectations. As a result, perception becomes subjective, bending reality to fit what you mentally anticipate. Additionally, zodiac compatibility can influence how individuals interpret social cues and interactions, further affecting perception. This influence demonstrates how powerful your mind is in constructing your visual experience, sometimes creating illusions even when the stimuli are straightforward.
Cognitive Biases and Visual Illusions

Your perception often warps reality without you realizing it, influenced by subconscious biases and expectations. These biases shape how you interpret visual cues, making what you see different from what actually exists. Understanding how your judgment is affected can help you see beyond illusions created by light, shadow, and mental filters.
Perception Warps Reality
Perception often distorts reality more than most realize, as the brain interprets sensory information through cognitive biases and visual illusions. These mental shortcuts and tricks can cause you to see things that aren’t there or misjudge what’s real. For example, you might:
- Overlook important details due to the *confirmation bias*, making you see what aligns with your beliefs.
- Misjudge distances because of *size illusions*, like the Ames room trick.
- Be fooled by *color and brightness illusions* that distort perception of shade and hue.
These distortions reveal how your mind filters reality, often prioritizing simplicity over accuracy. Consequently, what you perceive may be far from the truth, highlighting how perception actively warps reality.
Expectation Shapes Sight
When your mind anticipates what it expects to see, it can considerably influence what you actually perceive. This mental shortcut, called a cognitive bias, tricks your brain into filling in gaps or interpreting ambiguous images in line with your expectations. For example, if you’re told to look for a specific shape or pattern, your brain often sees it—even if it’s not really there. This happens because your brain prefers familiar or probable interpretations, shaping your visual experience. Expectations also cause you to overlook details that don’t fit your assumptions. As a result, your perception becomes biased, and illusions emerge. By understanding that your mind actively constructs what you see based on expectations, you recognize how perception isn’t purely objective but shaped by mental shortcuts and prior knowledge.
Biases Influence Judgment
Cognitive biases can distort your judgment even when you think you’re being objective. These mental shortcuts influence how you interpret visual illusions, often leading you astray. For example, you might:
- Trust your instincts over evidence, causing you to see illusions as real objects.
- Overlook context, making you misjudge size, depth, or distance.
- Favor familiar patterns, which can lead to illusions based on your past experiences.
These biases shape your perception, making illusions more convincing than they appear. Recognizing them helps you understand why your brain can be fooled—even when you’re trying to see clearly. By being aware, you can better differentiate between reality and illusion, sharpening your judgment in everyday life.
The Brain’s Construction of Reality
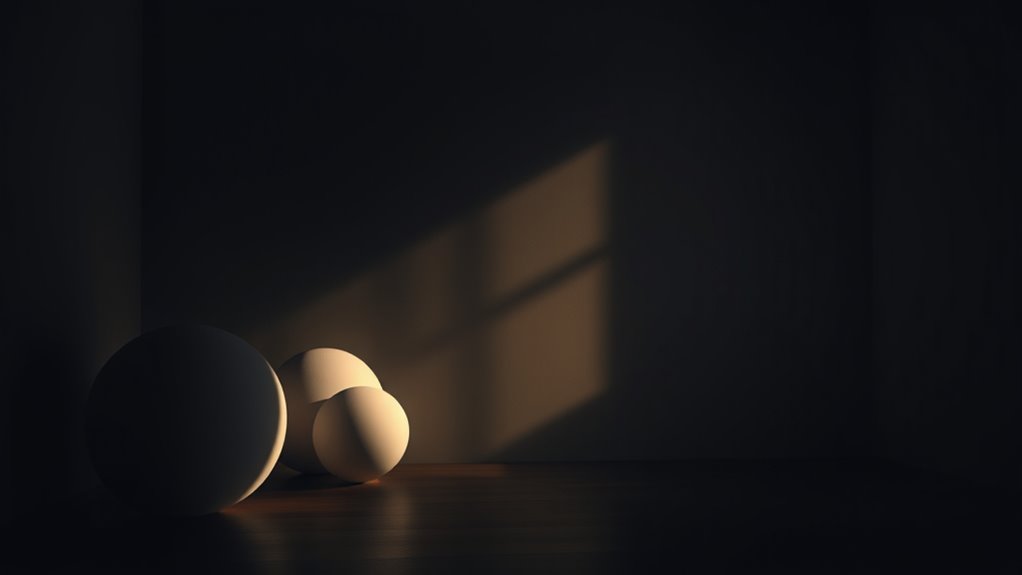

Your brain actively constructs your reality by interpreting signals from your eyes, ears, and other senses. It filters, combines, and sometimes distorts these inputs, creating a cohesive experience. This process explains why illusions deceive you; your mind fills in gaps based on expectations and past experiences. The following table illustrates how perception shapes your reality:
| Sensory Input | Brain Processing | Perceived Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Light & Shadow | Interpretation based on context | Visual illusions |
| Sound | Pattern recognition | Auditory illusions |
| Touch | Expectations & memory | Tactile illusions |
| Smell & Taste | Memories influence perception | Olfactory & gustatory illusions |
Your reality isn’t purely external—it’s a mental construction influenced by your senses and mind’s interpretations.
Classic Illusions and Their Underlying Principles
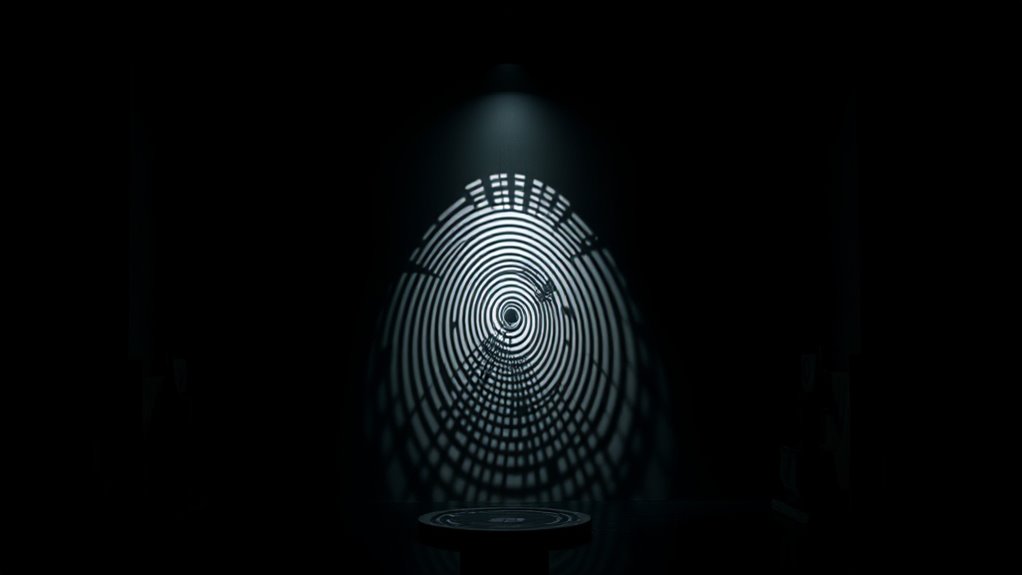

Classic illusions reveal how our visual system relies on specific principles to interpret what we see, often leading us astray. These illusions highlight key mechanisms:
Illusions expose how our visual system’s assumptions can mislead perception.
- Size and distance cues – how our brains judge object size based on context, causing illusions like the Müller-Lyer illusion.
- Contrast and shading – how shadows and light affect perceived depth and shape, seen in the Kanizsa triangle.
- Perceptual assumptions – our tendency to fill in gaps or assume continuity, evident in the Rubin vase.
Practical Applications of Light and Shadow in Art and Design
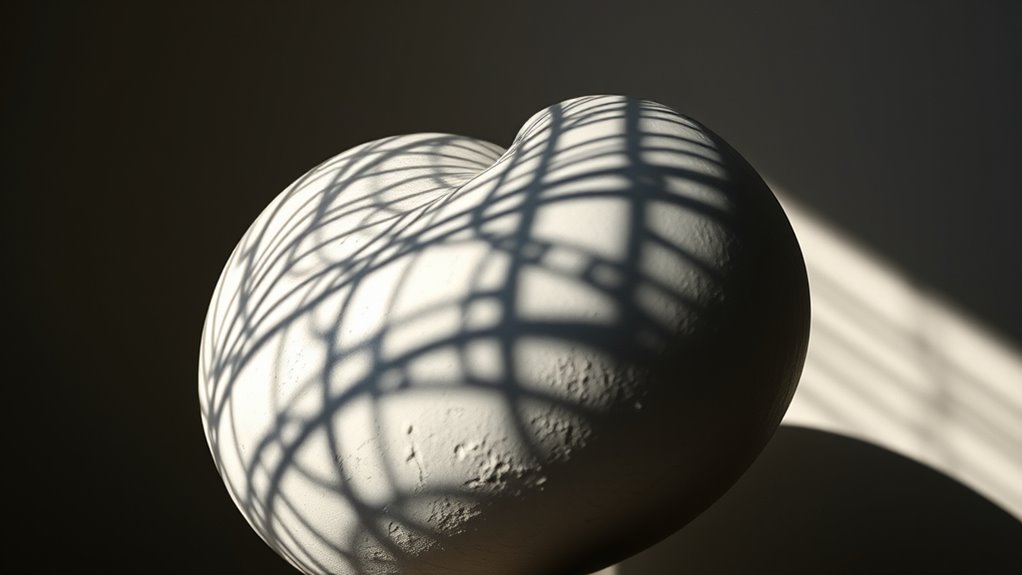

Light and shadow are powerful tools artists and designers use to create depth, focus, and mood in their work. By manipulating light sources and shadow placement, you can guide viewers’ attention, emphasizing key elements or creating a sense of mystery. For example, high contrast lighting can make objects appear more dramatic or intense, while softer shading produces a calm, inviting atmosphere. In interior design, strategic lighting highlights architectural features or sets a specific tone, influencing how spaces are perceived. In visual arts, chiaroscuro techniques dramatize scenes and add three-dimensionality. In branding and advertising, cleverly used shadows can evoke emotion or suggest movement. Overall, understanding how to control light and shadow allows you to craft compelling visuals that communicate your intended message effectively.
Exploring the Limits of Human Perception
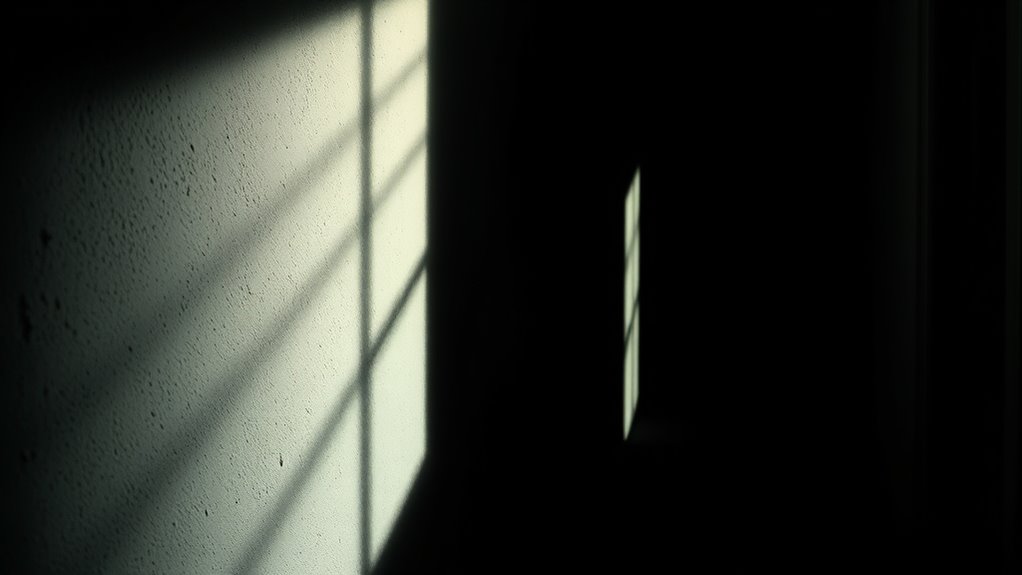

Human perception constantly pushes the boundaries of what we believe we see, often deceiving the eye through tricks of illusion and ambiguity. Your senses can be fooled in surprising ways, revealing how limited and malleable perception truly is. For example:
- Optical illusions challenge your assumptions about size, shape, and motion.
- Situations where shadows or context alter your interpretation of an image.
- Ambiguous images that flip between two or more interpretations, depending on focus.
These examples show that perception isn’t just passive reception but an active process shaped by light, shadow, and expectation. By understanding these limitations, you gain a deeper appreciation for how your mind constructs reality—and how illusions exploit that construction to deceive you.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Cultural Differences Affect Perception of Illusions?
Cultural differences shape how you perceive illusions because your background influences what you expect to see. For example, your cultural experiences might lead you to interpret visual cues differently, making some illusions more or less convincing. You may also focus on specific details that others overlook. This means your cultural lens filters your perception, causing variations in how illusions are experienced across cultures.
Can Illusions Be Used Therapeutically to Treat Perception Disorders?
Yes, illusions can be used therapeutically to treat perception disorders. You might experience visual or perceptual exercises that leverage illusions to retrain your brain, helping you differentiate between real and false perceptions. These techniques can improve your cognitive flexibility, reduce anxiety related to perception issues, and enhance your overall understanding of visual cues. Working with a trained therapist ensures these illusions are tailored to your specific needs for effective treatment.
What Role Does Age Play in Susceptibility to Visual Illusions?
Age influences your susceptibility to visual illusions because your visual system evolves over time. Younger people may interpret illusions differently from older adults due to differences in neural plasticity, cognitive development, and experience. As you age, your brain adapts, affecting how you perceive light, shadow, and expectation. Consequently, your ability to recognize illusions varies with age, shaping how you process and interpret visual information across different life stages.
Are There Neurological Conditions That Alter Illusion Perception?
Yes, neurological conditions can alter how you perceive illusions. For example, conditions like schizophrenia or autism spectrum disorder may affect visual processing, making illusions more or less convincing. Brain injuries or strokes can also change perception by damaging areas responsible for visual interpretation. If you have such conditions, your brain might interpret illusions differently, highlighting the complex relationship between neural health and perception.
How Do Technological Illusions Differ From Natural Visual Illusions?
Technological illusions differ from natural visual illusions because they are intentionally designed using devices like screens, virtual reality, or augmented reality to trick your eyes and brain. While natural illusions rely on light, shadow, and expectation, technological illusions manipulate digital visuals, creating effects that can be more immersive or complex. You experience these illusions through gadgets, which can alter perceptions more precisely and dynamically than natural illusions ever could.
Conclusion
By understanding how light, shadow, and expectations shape what you see, you realize the mind can be your best friend or trickster. These illusions remind you that perception isn’t always reality—sometimes, it’s just a game of shadows and assumptions. Keep in mind that what you see isn’t always what’s real, and don’t let illusions fool you—sometimes, the truth is hiding in plain sight. After all, seeing is believing, but not always the whole story.